Back
Direct numerical simulation of gas-liquid multiphase flows - Development of a solver
During my Bachelor Thesis, I developed an unsteady three-dimensional incompressible Navier-Stokes solver on both staggered and collocated grids with finite volume method of discretization. Time integration was done using second order implicit three-time-level scheme. Interface was captured with an algebraic VOF method and CICSAM advection scheme. CSF was implemented to account for surface tension along with Kernel K8 convolution for curvature calculation. The developed solver was successfully validated using the lid-driven cavity, mixed convection in cavity, rotation of slotted disk, drop in shear flows, static drop and dynamic drop test cases. Based on the results from test cases, few modifications were made to the solver to improve the accuracy and convergence. CICSAM was replaced by STACS which in turn was replaced by HiRAC with pseudo-time stepping to effectively avoid unbounded solution. Kernel convolution was replaced by height function method to improve the accuracy of the curvature calculation. Hybrid deferred correction method was developed and implemented with QUICK scheme for convective terms to improve the convergence of the solver.
This project was carried out under the guidance of Prof. Ravikiran kadoli as part of my Bachelor Thesis. This work was also presented at 5th International and 41st National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur (IITK), India, Dec 2014.
C language was used for development of the solver.
Post processing for all the cases was done using MATLAB, Techplot 8 and Paraview.
1. Navier-Stokes solver - Lid-driven cavity
After the development of Navier-Stokes solver, an improved deferred correction method which predicts using the power-law scheme and corrects with the QUICK scheme to interpolate convective terms was developed to obtain better convergence. Lid-driven cavity test case was used to validate the solver. Results were compared for Reynolds number 1, 100, 400, 1000, 3200, 5000, 7500, 10000 and a streamline plot for Re 1000 is shown below at 100th second (physical time).
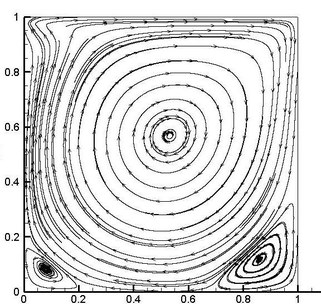
Lid driven cavity at Re 1000
2. VOF solver - Static drop in equilibrium
After the implementation of the algebraic VOF solver with CSF, a static drop in equilibrium was studied. A static drop within a domain of 8x8 with 40X40 cells is shown below at 0.001 secs. Max velocity of parasitic currents was found to be 0.051 m/s for Kernel convolution and 0.0143 m/s for height function method.
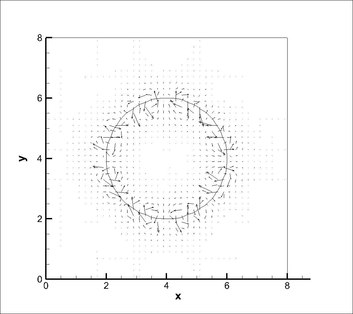
Kernel Convolution
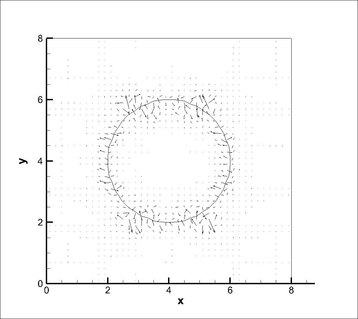
Height Function
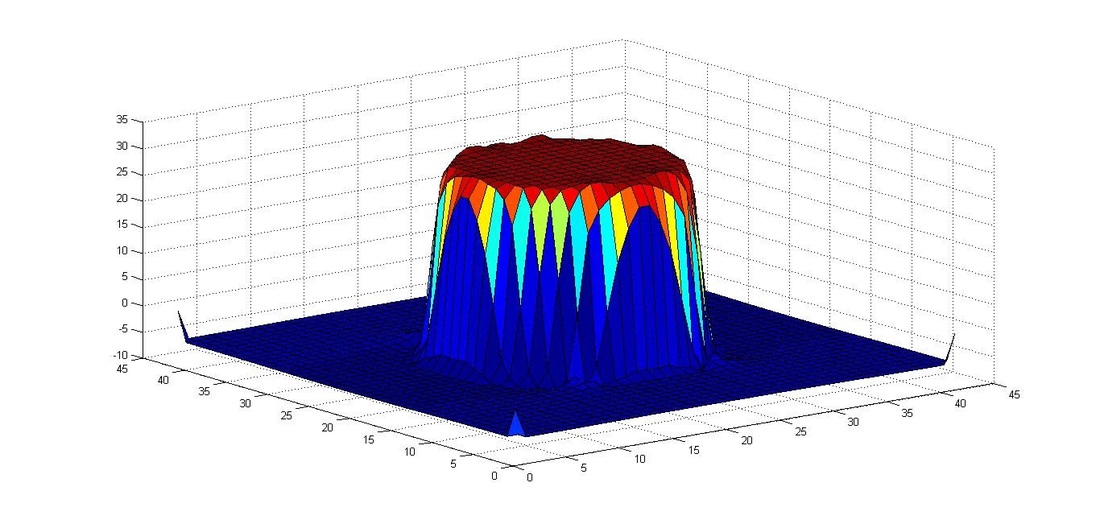
Pressure jump inside the drop (Height function)
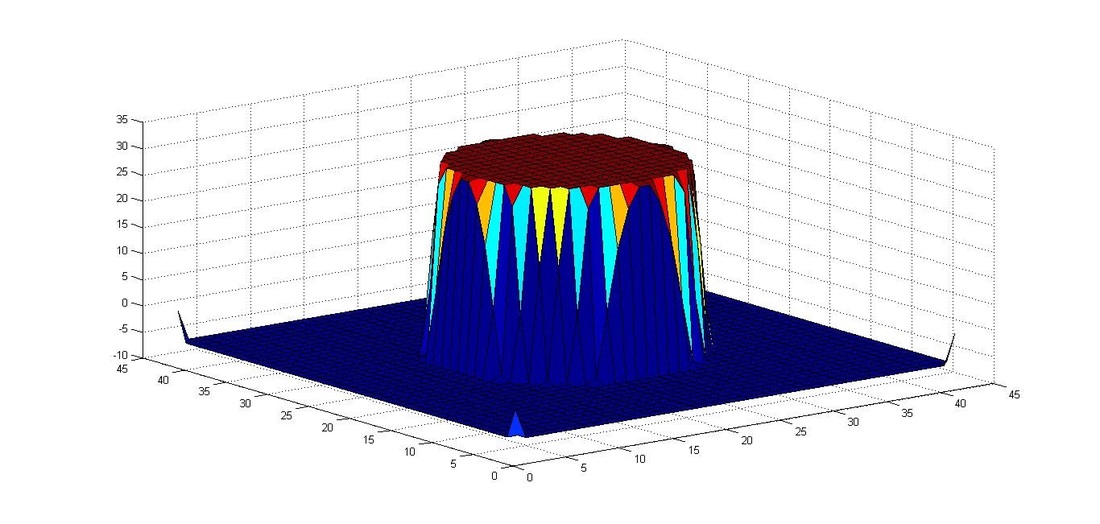
Pressure jump inside the drop (exact curvature)
3. VOF solver - Rotation of a slotted disk
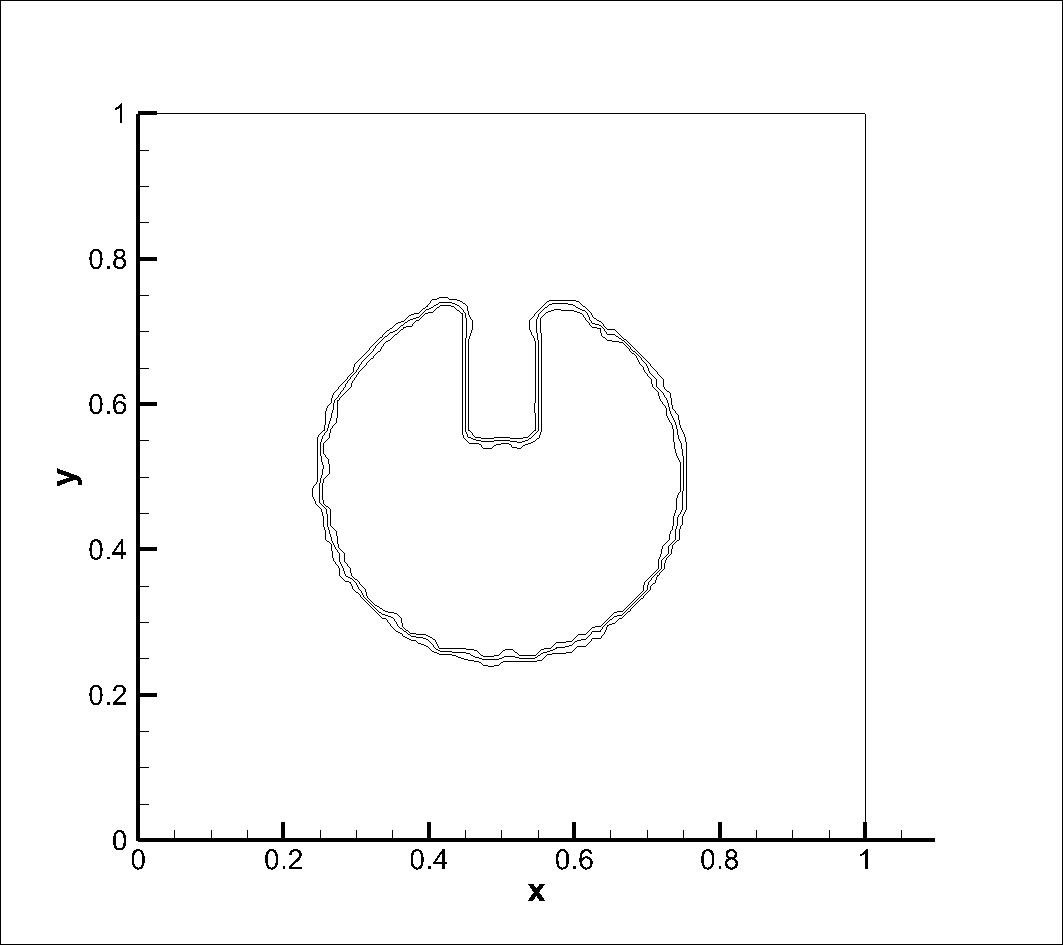
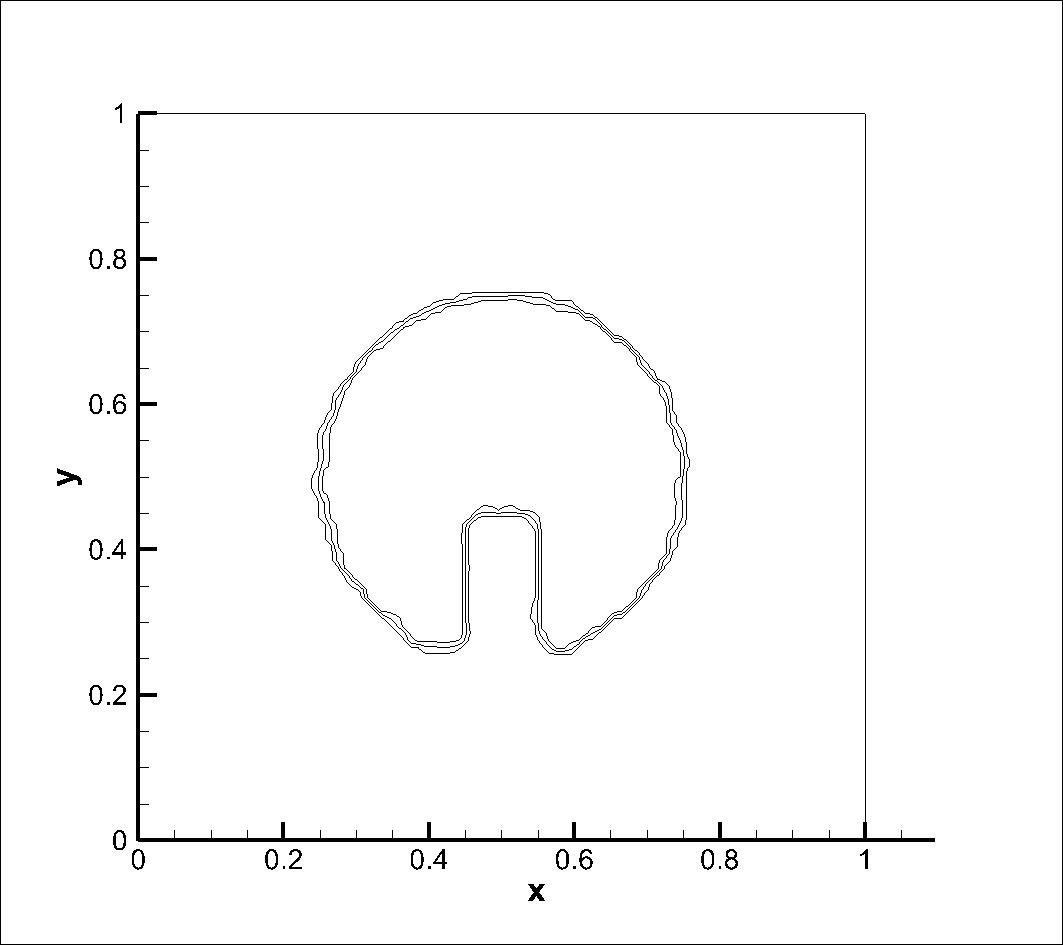
A circle with a slot is exposed to a circular velocity field. The mesh size of 100x100 was used, with the centre of the circle at (0.5, 0.5) and the centre of rotation at (0.5, 0.5). Simulation was performed at a courant number of 0.25. Results obtained using CICSAM and STACS were almost same at Courant number (Co) 0.25 and STACS performed better at Co 0.9.
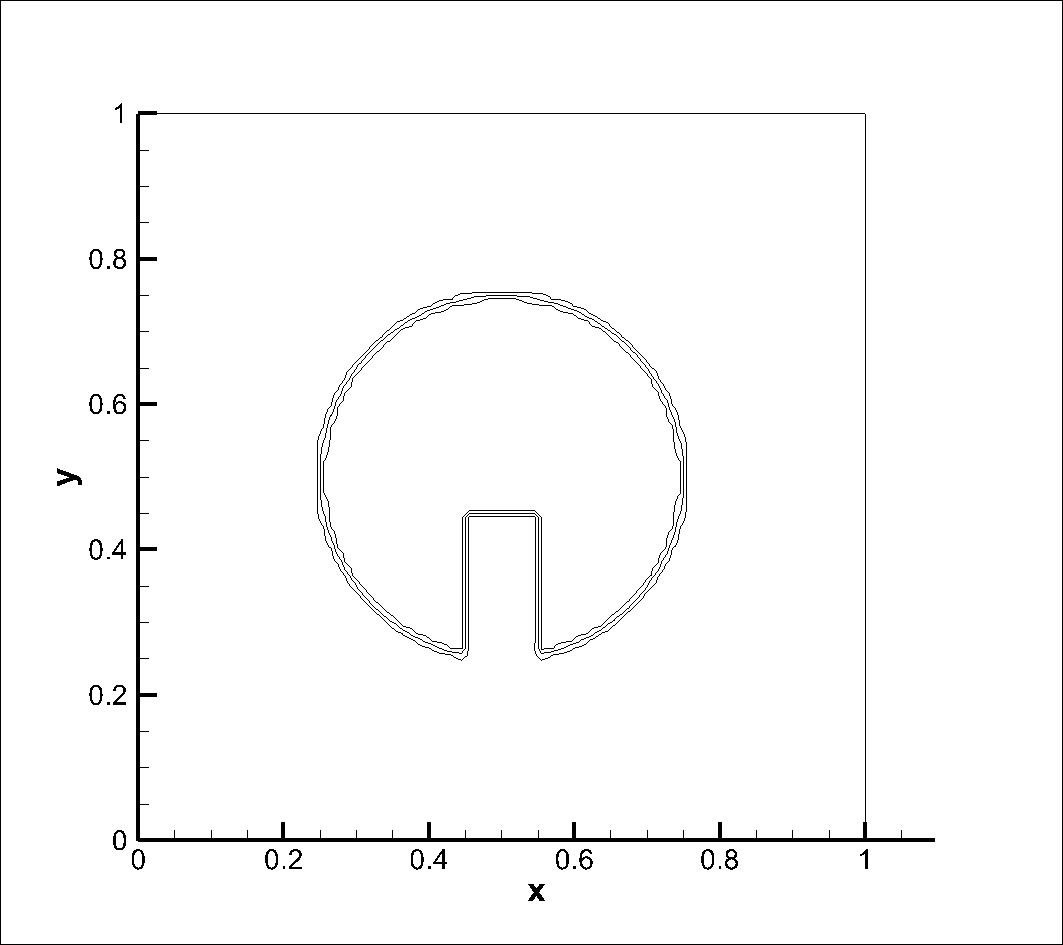
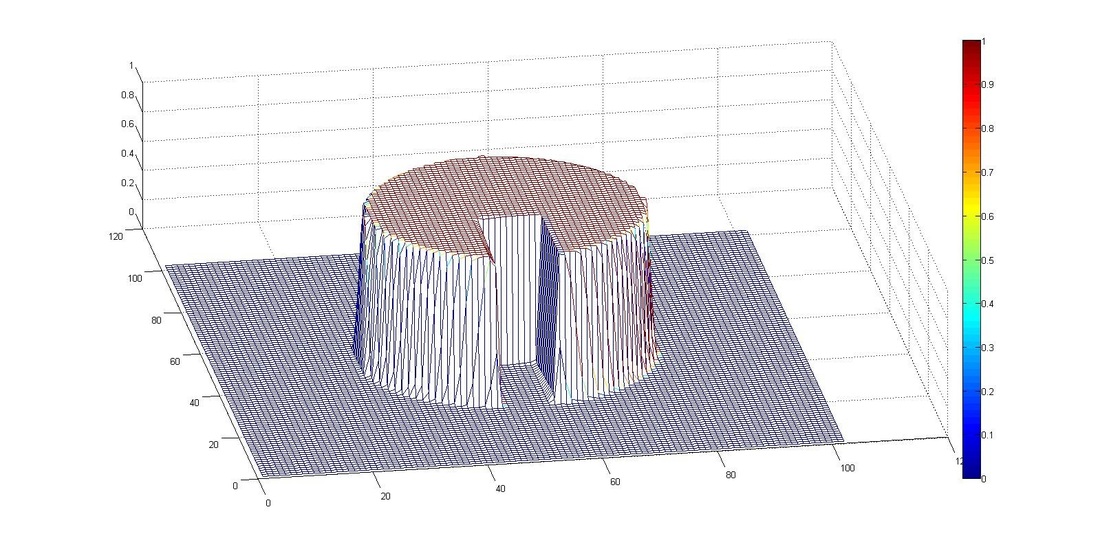
Initial Condition
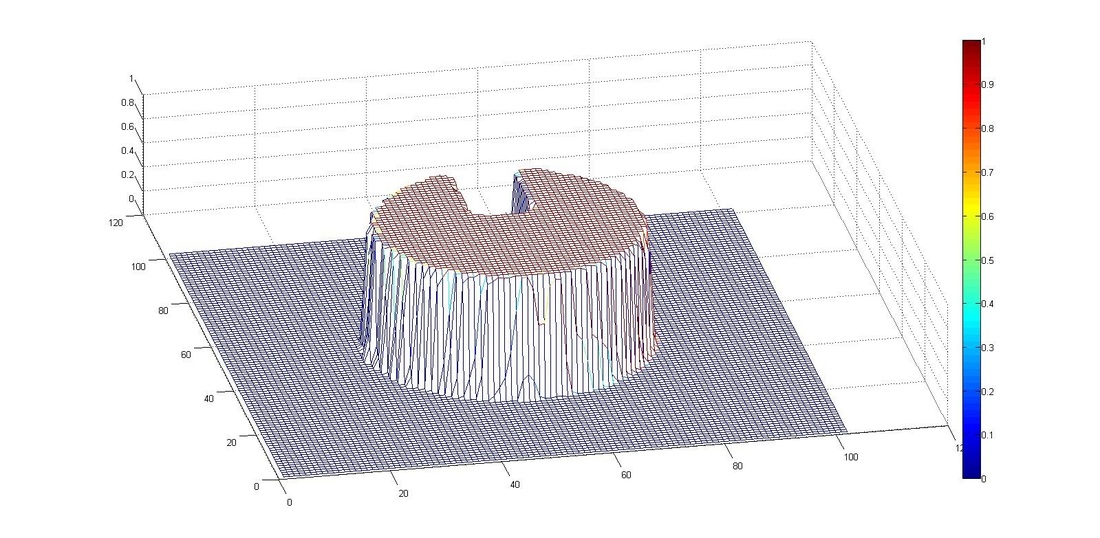
After Half Rotation
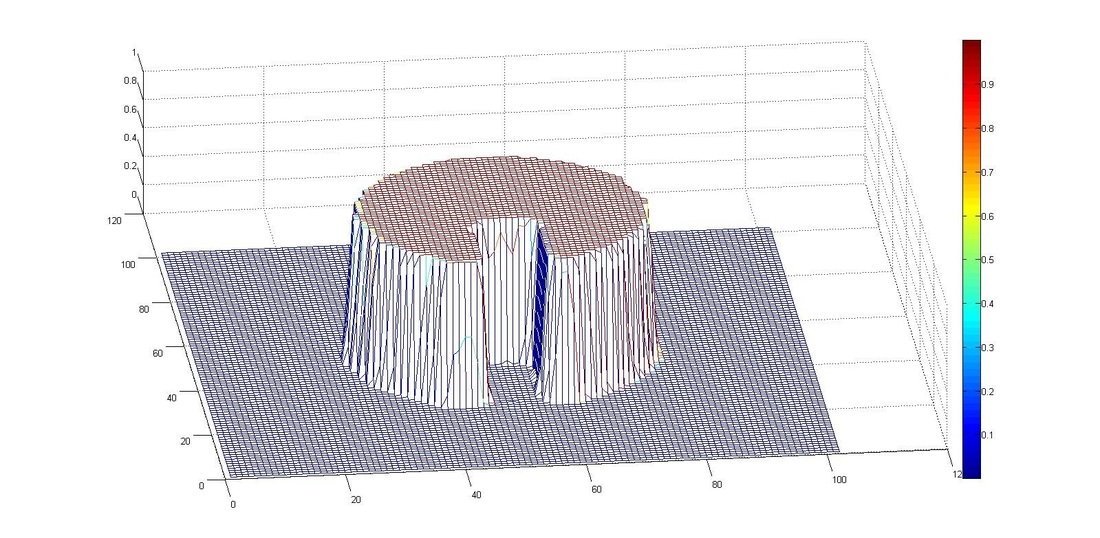
After One Full Rotation
4. VOF solver - Round drop in shear flow
A droplet is placed off centre in a rotating shear flow field. After one rotation, the flow field is reversed with an aim of recovering the original round droplet. The mesh used was 50x50 cells and the simulation was carried out for 5 seconds with reversal of velocity field at 2.5 seconds.
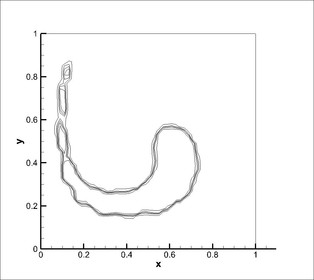
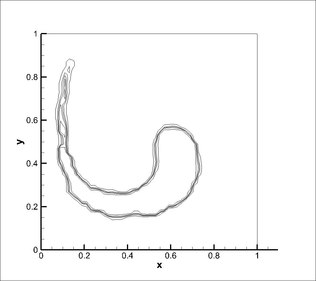
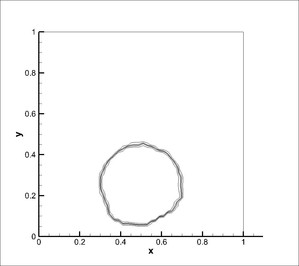
CICSAM
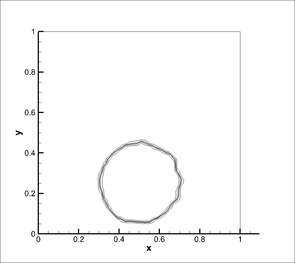
STACS