Today: variables, digital images, RGB color, for loop
CS106A doe not just teach coding. It has always taught how to write clean code with good style. Your section leader will talk with you about the correctness of code, but also pointers for good style. (from end of lecture-3, did not get to)
All the code we show you will follow PEP8 which is the Python standard for superficial things like spacing and whatnot.
See our Python Guide Style section. We'll pick out a few things today (for hw1), re-visit it for the rest later.
The HW problems are not that easy. Can take hours. It's not just you!
But we hope, once you have it working, you understand it, then could do it more easily. Like if your homework were deleted, you could do it again pretty readily.
See the Python Guide Variables chapter for more details.
A Python variable has a name and stores a value. We'll start with three rules of variables.
A variable is created in the code by a single equal sign = like this which creates a variable named x:
x = 42
The variable x is set at the moment the line runs.
Suppose there is also a line that sets a variable named color:
color = 'green'
Each variable is stored in the computer's memory. Think of the variable as a little box, labeled with the variable's name and containing a pointer to the value stored:
Suppose code sets a variable color to 'green'. On subsequent lines, appearances of the word color will retrieve the stored color. So for example, these lines paint two squares green:
color = 'green' bit.paint(color) bit.move() bit.paint(color)
The variable, color, is set on the first line, and then two later lines use it by its name. Note that the variable name does not have quote marks around it, just appearing as a bare word in the code.

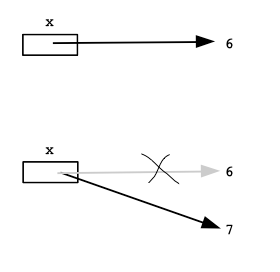
If a variable already exists, using = to change the variable simply changes the variable to refer to the new value. The old value is forgotten. Later references to the variable will use the new value. The = is like the phrase: "Now point to"
So in this example, the first paint is green, but the second is red
color = 'green' bit.paint(color) bit.move() color = 'red' bit.paint(color)

In memory, the variable points to 'green' and then, midway through the code, is changed to point to 'red'.
Mathematics: In mathematics, the equal sign sets up a permanent equality. Not so in code! In code, the = sets the variable to something, but it can be changed to something else with the next =.
Recall that "expression" is a phrase of code that represents a value. When it runs, that Python "evaluates" the expression to get a value at that point in the code.
You would think that computer programs have a lot of math at their core. It's true! Python can evaluate mathematical expressions, like a calculator can. Python follows the order of operations, so multiplication and division (* /) are evaluated before addition and subtraction (+ -). Other than that, the math is done from left to right. The math here looks a lot like regular mathematics, so we're not going to spend a lot of time explaining it.
1 + 2 * 3
Following the order of operations, Python evaluates the above expression to 7, doing the multiplication before the addition. We can visualize this as an arrow coming out of the expression:
Variables work naturally within expressions. In this example, the variable x is 5 within the expression.
x = 5 1 + 2 * x * 3
The expression evaluates to 31.
The Python "interpreter" is a program on your laptop which makes Python work on your laptop. More details later on that. However, there is a way you can type code right at the interpreter to see what it does.
Try the >>> interpreter on the experimental server - there's a button for this at the bottom of each problem page on the experimental server. You type a little expression at the ">>>" prompt and hit the enter key. Python evaluates it, prints the resulting value on the next line. We'll use this more as we get into more Python features.
So the ">>>" is the Python interpreter. You type Python code to it directly, see what it does. Not a good way to get work done, but an excellent way to try little phrases of code to see what they do.
We can use the interpreter to try out the claims about variables and math expressions.
>>> x = 11 >>> x 11
>>> 4 + 2 * 5 + 1 15
>>> x = 6 >>> 1 + 2 * x # evaluates to what?
The answer is 13. The appearance of x in the expression is just an example of a variable - Python retrieves whatever value was set to that variable, in this case 6.
>>> x = 6 >>> x 6 >>> 1 + 2 * x 13 >>> x = 7 # change x >>> 1 + 2 * x 15
Changing a variable changes it to point to a new value. After that, uses of the variable use the new value.
Or here is an example with numbers
x = 6 # x is 6 ... x = 7 # now x is 7 ...
We're not doing this one in class, but you can try it on your own to see a variable in action.
> all-blue
Go back to our all-blue Bit loop. Change the code to use a color variable as below. The variable color is set to hold the value 'blue', and the later lines just paint whatever color is in the color variable. This version paints the whole row blue.
def all_blue(filename):
bit = Bit(filename)
color = 'blue'
bit.paint(color)
while bit.front_clear():
bit.move()
bit.paint(color)
bit.right()
Look at the lines bit.paint(color) lines - they refer to the variable by its name, following the arrow to retrieve 'blue' or whatever was stored there.
Q: How would you change this code to paint the whole row red?
A: Change line 3 to color = 'red' - the later lines just use whatever is in the color variable, so now they will paint red with no other change.

Live RGB explorer: rgb-explorer
Roses are 255 0 0 Violets are 0 0 255 ...
This line loads an image into Python memory, and sets a variable named image to point to it, ready for Python to work on it.
# Load an image from the filesystem
# into memory in variable named "image".
# Now the image can be manipulated by code.
image = SimpleImage('flowers.jpg')

Say we have loaded an image variable as shown above. Now we want to write code to change the image in some way.
For example, let's say we want to set the blue and green values in each pixel of the image to 0. This will leave just the red values. This is called the "red channel" of the image - an image made of just its red lights.
pixel.red = 255Suppose we have a variable pixel that refers to one pixel inside an image. (We'll show how to obtain such a pixel variable in the next step.)
Then the syntax pixel.red or pixel.blue or pixel.green refers to the red or blue or green value 0..255 inside the pixel.
The example code uses = to set the red and blue values of the pixel to 255 and the green value to 0. This changes the pixel to be magenta.

If we take an image, and turn off all the green and blue light but leave the red lights on. This makes the "red channel" image:
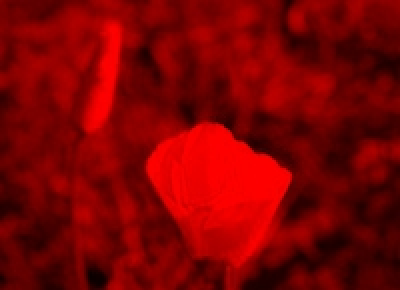
Similarly, we can make the green and blue channels:

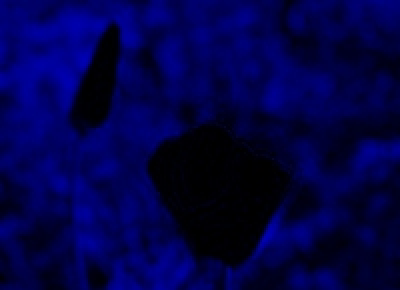
We'll use these in a minute as an example.
The for-loop is probably the single most useful loop we'll see. Say you have a collection of 1000 urls. The for-loop lets you write a few lines of code, and then run those lines once for each url or whatever is in the collection. This is sometimes called a "for each" loop, since it runs the code once for each element. Being able to run some code once for each element in a collection is very handy, and this is exactly what the for loop gives us.
for variable in collection:
# use variable in here
The "red channel" of an image is just the red lights, with blue and green all turned off. Here is the code to make the red channel of an image using a for loop.
def red_channel(filename):
image = SimpleImage(filename)
for pixel in image:
pixel.green = 0
pixel.blue = 0
return image
Here is a link - you can try running it first, then we'll see how it works
The most important element in the for loop is the variable which comes after the for. The for-loop takes control of the variable, setting it to point to the next element for each run of the loop body.
For the red-channel example, the loop sets the pixel to point to the first pixel in the image and runs the loop body. Then it sets pixel to point to the second pixel and runs the loop again. And so on, running the body once for each pixel in the image. If the image has 50,000 pixels, the loop body runs 50,000 times, once for each pixel in the image.
for pixel in image:
# "pixel" points to the next pixel
# each iteration of the loop
pixel.green = 0
pixel.blue = 0
The programer just uses the variable in the loop for their desired computation, knowing that the for loop will set the variable to point to every element, one per run of the loop body.
Side trip about math
x = x + 1What does this do:
x = 6 x = x + 1
x = 6 x = x + 1
for pixel in image:
pixel.red = pixel.red * 0.5
pixel.green = pixel.green * 0.5
pixel.blue = pixel.blue * 0.5
# or shorthand form:
# pixel.red *= 0.5
Say we have this
x = x + 1
That can be written in shorthand like this:
x += 1
If we have this
x = x * 2
Shorthand form:
x *= 2 # double x
For these image problems, that looks like
pixel.red = pixel.red * 0.5 # long form pixel.red *= 0.5 # shorthand for above
>>> x = 10 >>> x += 3 >>> x 13 >>> x *= 2 >>> x 26
The image1 section is all image problems solved with a for loop to do some operation on every pixel in the image.
Loop over the image, write code to change pixels, recovering the hidden image. Nick solves part, then students try to type code for the rest.
5-10-20 puzzle: The red, green, and blue values are too small by a factor of 5 10 20. But we do not know which factor goes with which color. Figure it out by experimenting with code to modify the image with various factors (i.e. guessing and running it).
> The image1 section has problems like this. The the Iron Puzzle.
Now we can look at the coordinate system of the pixels.
The pixels are arranged in an x, y grid, so we can identify each pixel by its x, y coordinates. We write the two numbers as the x value followed by y, as usual for mathematics. The origin x=0 y=0, aka (0, 0) is the upper left pixel.
The x values increase going left-right as usual - so the leftmost column of pixels is x=0, the next column is x=1, and so on.
The y values increase going down which is different from usual. The topmost row of pixels is y=0, the next row down is y=1, and so on. This ordering, y growing down, is akin to reading English text, with the lines running from top to bottom.
We'll build up techniques below, and our goal is using the range() function and nested loops to go through all x,y of an image.
Here is a diagram of an image of 6 pixels width and 4 pixels height. First we'll look at the x and y numbers for all the coordinates.
The pixels are numbered starting with 0 - "zero based indexing". This is an incredibly common scheme within computers, so you'll get used to it. Zero based indexing makes the math come out cleaner for some cases, which is why it is used in code.
Look at the top row of pixels.
The first pixel is at x=0, the next is x=1, and so on up to x=5 for the last pixel at the right side.
Key it's easy to think — well it's width 6 so the rightmost pixel is at x = 6. Nope! In zero based indexing, the last index is 1 less than the number of things — 6 pixels, last pixel is index 5, aka last pixel is at x = (width - 1)
6 pixels -> index numbers 0..5
10 pixels -> index numbers 0..9
More generally, if you have n things with zero-based indexing, the first is at 0 and the last is at n - 1.
This is not deeply difficult, but it's an easy "off by one error" (OBO) to make. We'll talk about OBO more later.
range(n) FunctionSee the Python Guide range
range(10) -> [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] range(6) -> [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] range(3) -> [0, 1, 2] range(n) -> [0, 1, 2 .... n-1] # UBNI Start at 0, go up to but not including N
Demo (or you can try it). The print(xx) function in this context just prints out what is passed to it within the parenthesis. Normally we indent by 4 spaces, but it's ok to just indent by 2 spaces in this temporary, on-the-fly context.
>>> for x in range(10):
print('in loop:', x)
in loop: 0
in loop: 1
in loop: 2
in loop: 3
in loop: 4
in loop: 5
in loop: 6
in loop: 7
in loop: 8
in loop: 9
1. We see that the for loop works with range(), running the body once for each number.
2. Try different numbers as the parameter passed in to range(). (Use up-arrow in the interpreter to recall previously typed lines - a great time saver.