At the start of the quarter, we laid out the following learning goals that we hoped to achieve:
- writing C programs with complex use of memory and pointers
- an accurate model of the address space and compile/runtime behavior of C programs
- translating C to/from assembly
- writing programs that respect the limitations of computer arithmetic
- identifying bottlenecks and improving runtime performance
- working effectively in a Unix development environment
- using ethical frameworks and case studies to inform decision-making
- a working understanding of the basics of computer architecture
Here's a look back at how we worked to achieve these learning goals via the different topics we covered, and why they're important.
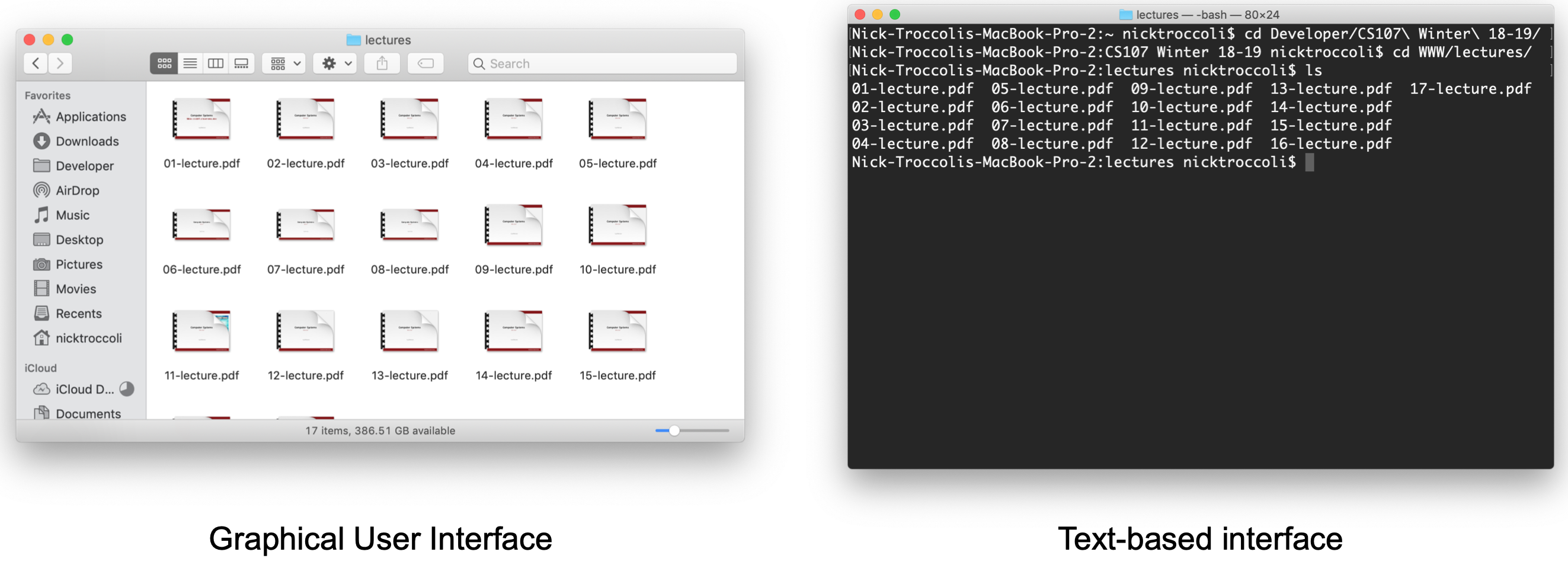
Unix, Command Line and C

How can we use the command line and C to write, compile and run our programs?
Writing, Testing, Debugging and Profiling Code
(gdb) r input.txt
...
How can we write programs with good style, create comprehensive test cases and use tools such as GDB and Valgrind to debug and profile our code?
Topic 1: Bits and Bytes
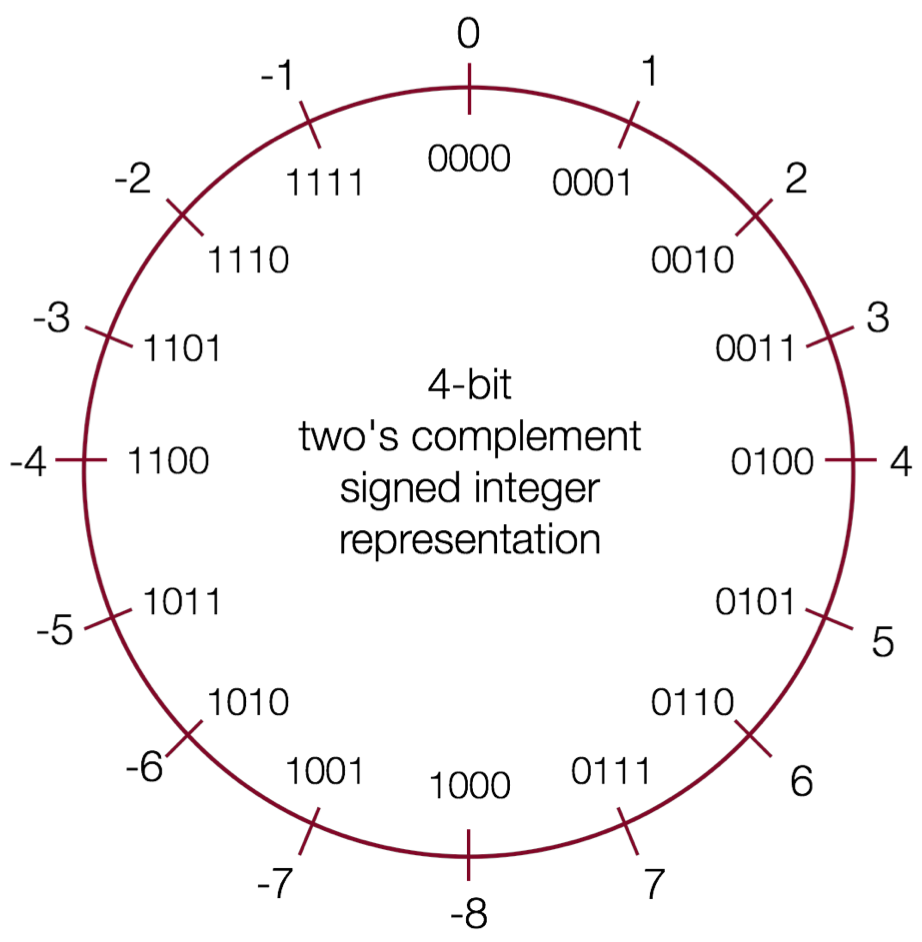
How can a computer represent integer numbers?
Topic 2: Chars and C-Strings
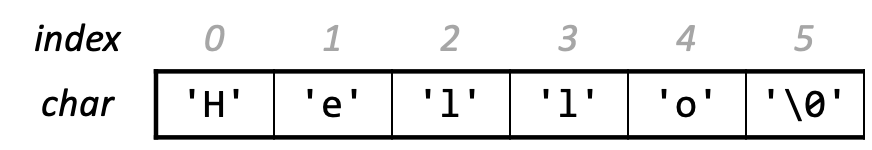
How can a computer represent and manipulate more complex data like text?
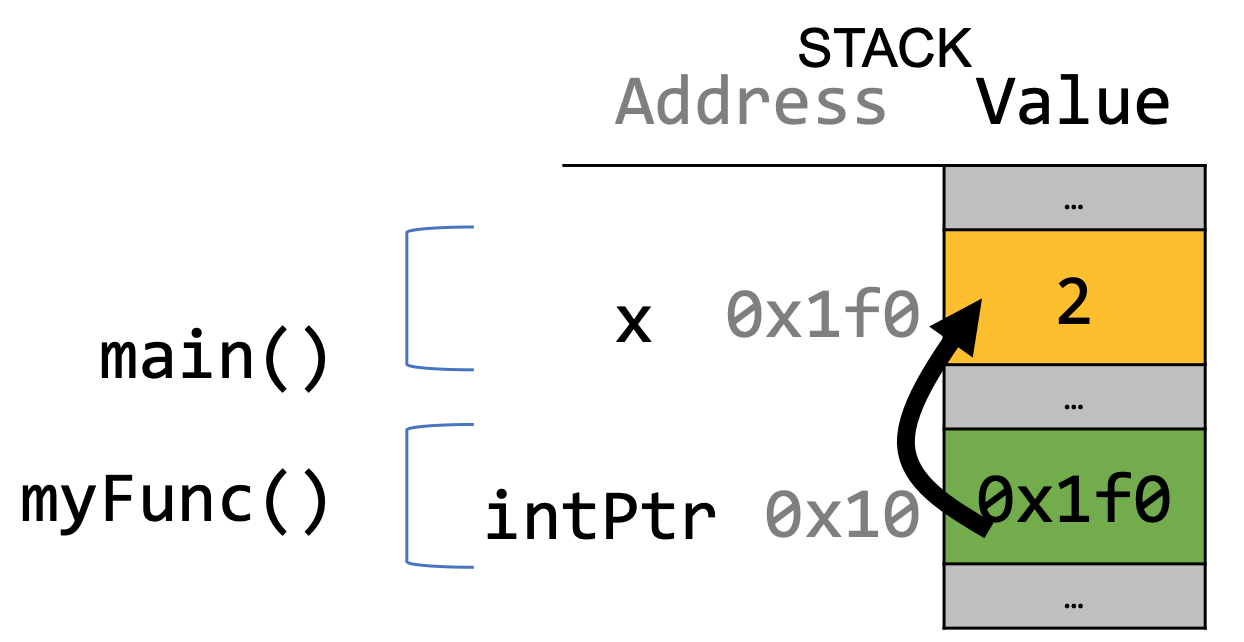
Topic 3: Pointers, Stack and Heap
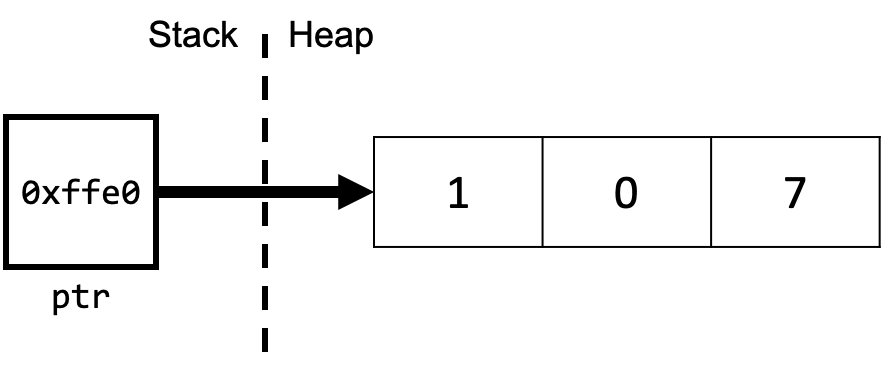
How can we effectively manage all types of memory in our programs?
Topic 4: Generics
memcpy(dst, src, size)
cmp_fn
How can we use our knowledge of memory and data representation to write code that works with any data type?
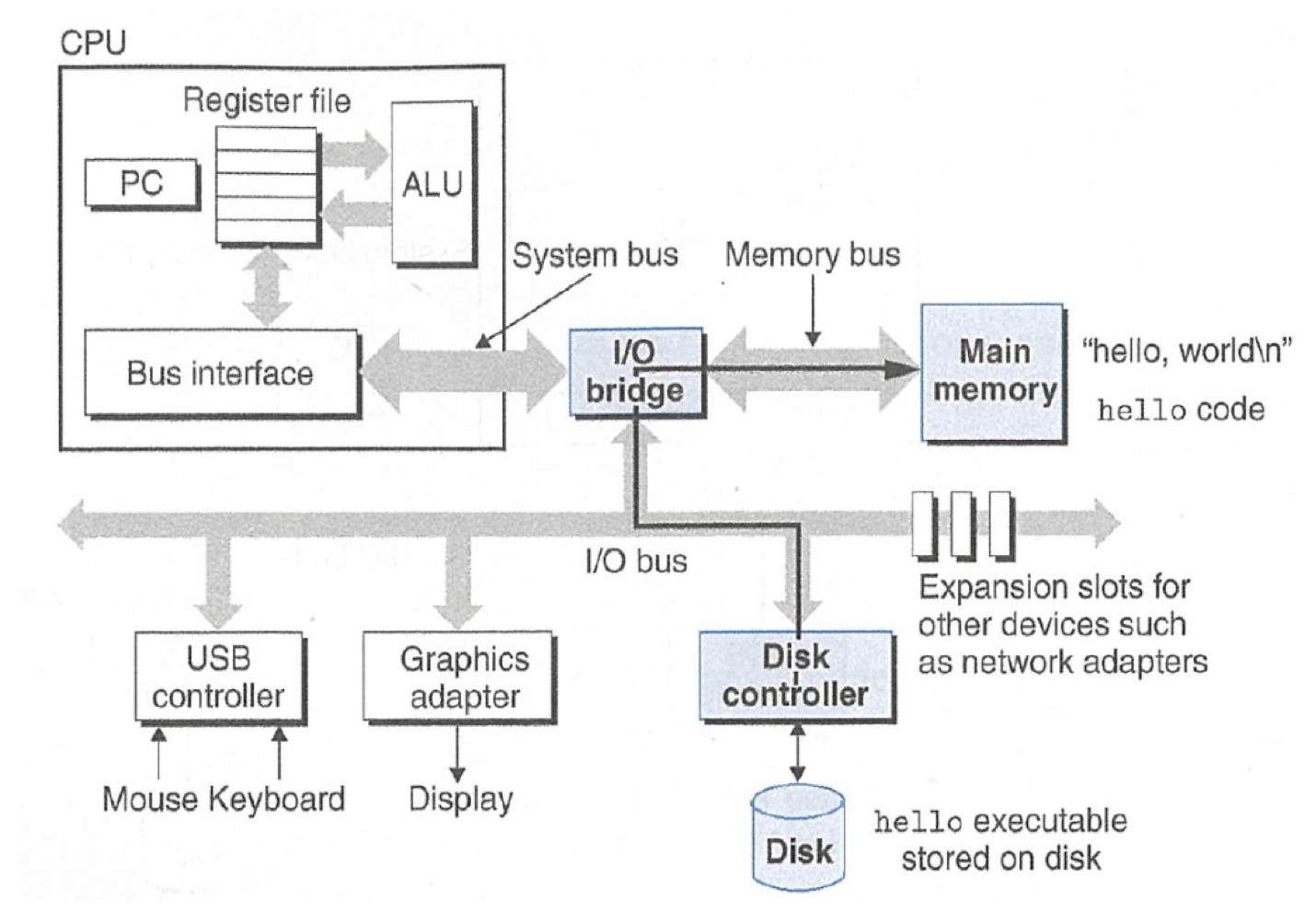
Topic 5: Assembly
test %rbx, %rbx
jle 0xffe2c
How does a computer interpret and execute C programs?
Topic 6: Heap Allocators
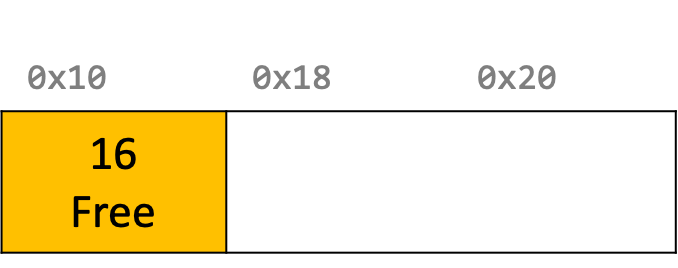
How do core memory-allocation operations like malloc and free work?
Interwoven Topic: Ethics
How do we act responsibly in maintaining security, protecting privacy, and ensuring warranted trust in the systems we build and maintain?