Jupyter
From FarmShare
(start of revision to jupyter) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | == Jupyter == | |
| + | [https://jupyter.org Project Jupyter] evolved out of the [https://ipython.org IPython] project (specifically the IPython notebook). The primary goal of Project Jupyter is to provide an interactive, web-browser driven, language-independent programming environment. Jupyter can be deployed on the farmshare servers to enable an accessible, powerful, and persistent computational platform. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === FarmShare Specific Features === | ||
| + | |||
| + | At the end of this guide, the resulting jupyter notebook will support: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * an SSL encrypted, password enabled, web-browser enabled programming environment | ||
| + | * persistence of the environment for seven days (maximum duration of [https://uit.stanford.edu/service/kerberos Stanford Kerberos] tickets | ||
| + | * file/data storage on the [https://uit.stanford.edu/service/afs Stanford AFS] servers with 5GB user quota and automatic backups | ||
| + | * shared file/data storage to [https://uit.stanford.edu/service/its-course-support/diskspace Class Disk AFS Space] | ||
| + | * simple switching to any of the [https://web.stanford.edu/group/farmshare/cgi-bin/wiki/index.php/Main_Page Stanford FarmShare] systems | ||
| + | * python2 support | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Installation === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Ipython == | == Ipython == | ||
Revision as of 14:23, 23 December 2016
Contents |
Jupyter
Project Jupyter evolved out of the IPython project (specifically the IPython notebook). The primary goal of Project Jupyter is to provide an interactive, web-browser driven, language-independent programming environment. Jupyter can be deployed on the farmshare servers to enable an accessible, powerful, and persistent computational platform.
At the end of this guide, the resulting jupyter notebook will support:
- an SSL encrypted, password enabled, web-browser enabled programming environment
- persistence of the environment for seven days (maximum duration of Stanford Kerberos tickets
- file/data storage on the Stanford AFS servers with 5GB user quota and automatic backups
- shared file/data storage to Class Disk AFS Space
- simple switching to any of the Stanford FarmShare systems
- python2 support
Installation
Ipython
Ipython provides both a command line and browser based (notebook) interfaces. The development is quite fast, so the distribution provided packages tend to lag behind enough it makes sense to setup a python environment which incorporates the latest updates.
building an Ipython notebook environment
Login to a corn and make yourself an Ipython environment in the non-AFS space
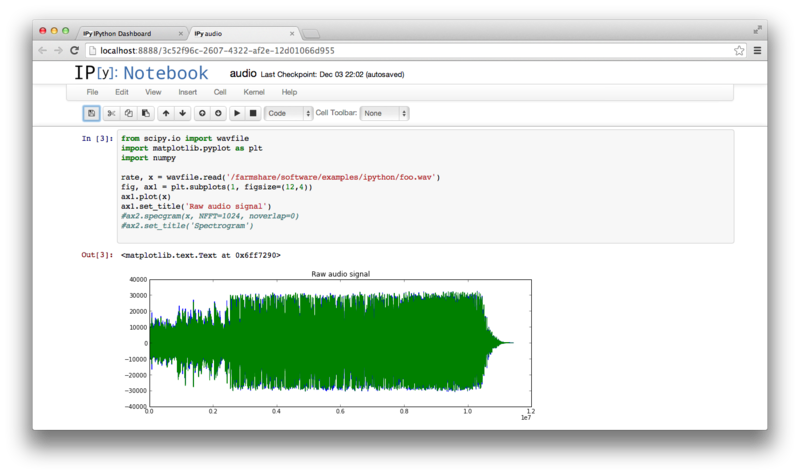
mkdir -p /farmshare/user_data/$USER/ipythontest cd /farmshare/user_data/$USER/ipythontest virtualenv --system-site-packages devbranch devbranch/bin/pip install --upgrade ipython devbranch/bin/pip install --upgrade tornado devbranch/bin/pip install jsonschema cp -p /farmshare/software/examples/ipython/audio.ipynb .
To run Ipython notebook environment, first start it up:
devbranch/bin/ipython notebook `%pylab inline` --no-browser
You should see output similar to following:
2013-12-03 21:39:50.435 [NotebookApp] Created profile dir: u'/afs/ir.stanford.edu/users/b/i/bishopj/.config/ipython/profile_default' 2013-12-03 21:39:50.465 [NotebookApp] Using MathJax from CDN: http://cdn.mathjax.org/mathjax/latest/MathJax.js 2013-12-03 21:39:50.599 [NotebookApp] Serving notebooks from local directory: /srv/zfs01/user_data/bishopj/ipyhtontest 2013-12-03 21:39:50.599 [NotebookApp] The IPython Notebook is running at: http://127.0.0.1:8888/ 2013-12-03 21:39:50.599 [NotebookApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation).
Setup an ssh tunnel from your desktop system to the same corn system you ran the notebook on in previous step. In my case port 8888 and corn02.
ssh -L 8888:localhost:8888 corn02
Now again from your desktop system open a web browser and navigate to 'localhost:8888'
Now click on Cluster and startup your cluster 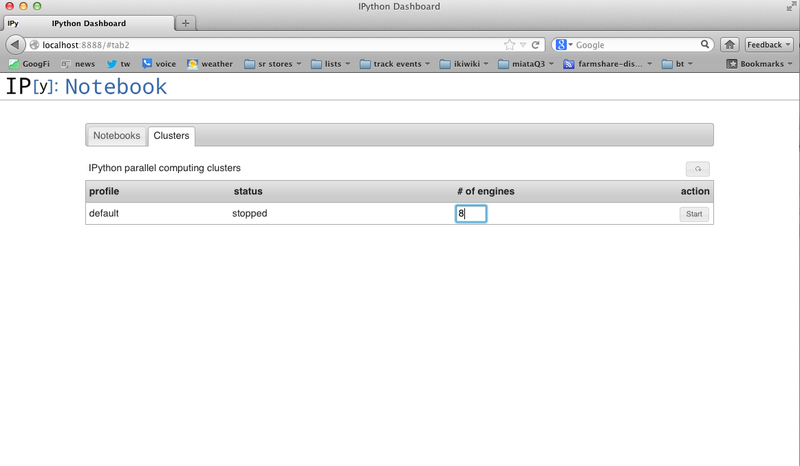
Click back on the Notebook tab and you should see an audio notebook. click on this.
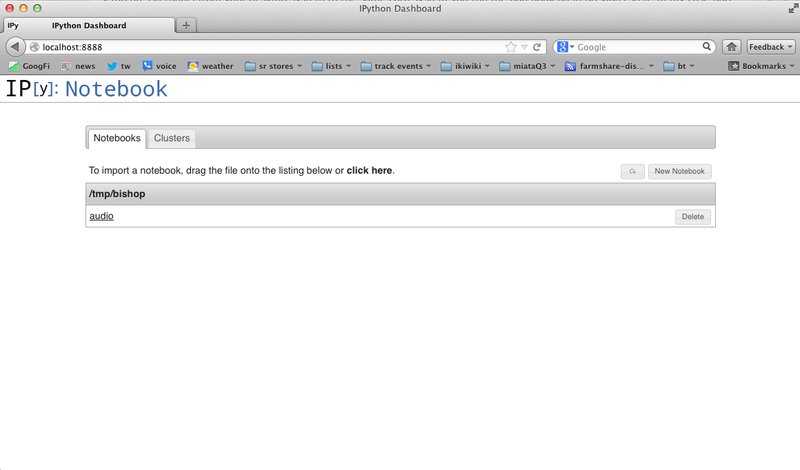
Now you can load up a notebook and "play"