CS106A Quiz #1 Review Materials
Quiz #1 Date: July 9th, 2021
Practice Exercises From Lecture and Section
For most of the problems below, you have watched someone walk through a solution, or you have solved it possibly glancing at a similar lecture example. Some of these will now seem very easy. That was fine then. But for the exam, you should be able to solve any of these without access to anything - just your knowledge of Python and maybe making a little drawing to think about your code. Below are section problems which make excellent practice. You should also be able to do the problems linked from each lecture, which often introduce the ideas then seen in section and on the homeworks.
Section Problems: all of the sections and their solutions are listed off our course page.
1. Bit
> go-green
> Fix Tree
> all-blue (while + front_clear)
> change-blue (while + if/get_color)
> bit-rgb (while + first/last square)
> double-move (while + two moves in loop)
> fix-tree (while-until-color, our make-a-drawing example)
> reverse-coyote (while + right_clear)
> standard-coyote (while + left_clear + not)
> climb (multiple whiles)
> reverse-santa (multiple whiles)
> standard-santa (multiple whiles)
> falling-water (multiple whiles, even/odd issue)
Examples with multiple functions working together:
> Hurdles
You should be familiar with your homework-1 solution code. The Checkerboard problem is a classic, difficult homework problem. However, we will note that quiz questions are typically smaller than the Checkerboard problem.
2. Image Loops
We're not doing the basic image-foreach, which we used in lecture to introduce images. The quiz will use nested-loop image code, like the homeworks.
> Mirror1
> Mirror2
> Red Wing
You should also be familiar with your own hw2 solution code.
3. Functions + Strings
In weeks two and three, we've introduced basic functions, basic strings, and Doctests. The quiz does not include the Grid, which we will use on homework 3.
You can access the lecture examples and some additional examples on basic functions and strings at the following link to the experimental server:
> Experimental Server Functions
Sample Questions
Here are a few sample questions, mostly drawn from old exams. These are representative, but you should be familar with all the lecture examples and homework problems. The quiz will have just 3 or 4 problems, appropriate for something so short.
Bit
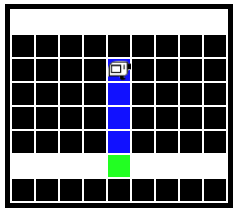
1. Bit is in a 1 square tall tunnel facing the right side of the world. Move bit forward zero or more squares until a clear square appears above - a chimney Paint the square below the chimney opening green. Move bit straight up the chimney until blocked, painting every moved to square blue.
Before:
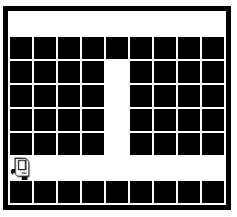
After:
def chimney1(filename):
bit = Bit(filename)
#your code here
pass
2. Bit is in a 1 square tall tunnel facing the right side of the world. Move bit forward zero or more squares until a clear square appears above - a vertical pipe. Move bit straight up the pipe until blocked, painting every other square green, starting with the square where bit notices the pipe.
Before:
After:
def chimney2(filename):
bit = Bit(filename)
#your code here
pass
3. Bit is in a world that contains a single rectangle of filled squares. Bit is to the right of the rectangle, facing a block on its right side as shown in this representative example:
Move bit forward to the edge of the rectangle. Then move bit down past the lower right corner of the rectangle. Finally, move bit to the left side of the world, painting every square occupied blue. Your code should work for any position and size rectangle, and bit will always start facing a block on the right side of the rectangle as in the example above.
def do_quiz(filename):
bit = Bit(filename)
# your code here
pass
Images
1. Given an image, create a new 'out' image which is three times as wide as the passed in image. Copy the original image to the rightmost third of the out image, but with left and right reversed.
def mirrorish(filename):
image = SimpleImage(filename)
# your code here
2. Given an image, and an int n, create a new 'out image' which is n pixels taller than the given image. Add an n pixel 'hat' to the out image that is colored magenta. Copy the original image but horizontally and vertically flipped below the n pixel hat.
def funky_hat(filename, n):
image = SimpleImage(filename)
# your code here
3. Given an image file and int margin that is 0 or more, create and return a new out image as follows (see diagram below). (a) The out image should be created as blank white image as usual, with space for two columns added at its sides, each with the width “margin”. The left column is blank, the right column is colored purple. The purple color can be made with green = 0, red and blue = 255 as on the homework. (b) Between the columns, there should be a top area the size of the original image which is left blank. (c) Below the blank area should be a copy of the image which is reversed horizontally but unchanged vertically.
In the diagram, each of the 4 areas is shown with a black border to show where the areas are. There are no black borders in the actual output. The boilerplate code is provided to the right, fill in the missing bits of code:
- Create the out image
- for y/x loop code to color in the purple columns
- for y/x loop code to copy in the reversed image
def wave(filename, margin):
image = SimpleImage(filename)
#### Part a Create out ####
pass
#### Part b Color in column ####
pass
#### Part c Copy in reversed ###
pass
return out
4. Given an image file and int parameters a and b which are 0 or more, create and return a new out image as follows (see diagram below). The out image should have a yellow rectangle a pixels wide and b pixels high at the top-left of the out image. Below the yellow rectangle, place a vertically flipped copy of the original image. The width of the original image will be greater than a, so the flipped image will be wider than than the yellow rectangle. Leave the area to the right of the yellow rectangle blank.
The outline of the code is provided, fill in the missing bits of code:
- Create the out image
- Color the yellow rectangle
- Copy the vertically flipped image
def do_image(filename, a, b):
image = SimpleImage(filename)
# a Create the out image
pass
# b Color the yellow rectangle
pass
# c Copy the vertically flipped image
pass
Functions
The lecture example functions are all representative quiz-type problems. Here are some examples.
digits_only(s): Given a string s. Return a string made of all the chars in s which are digits, so 'Hi4!x3' returns '43'. Use a for/i/range loop.
def digits_only(s):
pass
lastly(s, n): Given string s and int n which is zero or more. Return a version of the string with n copies of its last char added at its end. Use a for/i/range loop. If the string is too short to have a last char, return it unchanged.
def lastly(s, n):
pass
You could also have a question with this sort of function with Doctests, which would look like this. In this case, the Doctest is just a syntax for writing out the input and output of 1 test case.
>>> lastly('abc', 3)
'abcccc'
alpha2x(s): Given a string s. Compute a string with 2 copies of each “alphabetic” char in s. Recall that char.isalpha() tests if a char is alphabetic. Return the computed string with a ‘@’ added at its beginning and end.
So for example: alpha2x(‘ab12x’) returns ‘@aabbxx@’.
def alpha2x(s):
pass
alpha_start(s): Given a string s. Construct and return a string that,
for every alphabetic char in s, has that alphabetic char with an asterisk '*' in front of it. Ignore non-alphabetic chars. So for example, the string '$a@@bC66' returns '*a*b*C'. Use a for/i/range loop to look at every char in s.
Solution to Problem 3
def alpha_start(s):
pass
Solutions
Bit
def chimney1(filename):
bit = Bit(filename)
# You code here
pass
while not bit.left_clear():
bit.move()
bit.left()
bit.paint('green')
while bit.front_clear():
bit.move()
bit.paint('blue')
def chimney2(filename):
bit = Bit(filename)
while not bit.left_clear():
bit.move()
bit.left()
bit.paint('green')
while bit.front_clear():
bit.move()
if bit.front_clear():
bit.move()
bit.paint('green')
def do_quiz(filename):
bit = Bit(filename)
while bit.front_clear():
bit.move()
bit.left()
while not bit.right_clear():
bit.move()
bit.paint('blue')
bit.right()
while bit.front_clear():
bit.move()
bit.paint('blue')
Images
def mirrorish(filename):
image = SimpleImage(filename)
# your code here
out = SimpleImage.blank(image.width * 3, image.height)
# loop x,y over original image
for y in range(image.height):
for x in range(image.width):
pixel = image.get_pixel(x, y)
# key: locate pixel in out image
pixel_out = out.get_pixel(out.width - x - 1, y)
pixel_out.red = pixel.red
pixel_out.green = pixel.green
pixel_out.blue = pixel.blue
def funky_hat(filename, n):
image = SimpleImage(filename)
out = SimpleImage.blank(image.width, image.height + n)
for y in range(n):
for x in range(image.width):
out_pixel = out.get_pixel(x, y)
out_pixel.green = 0
for y in range(image.height):
for x in range(image.width):
pixel = image.get_pixel(x, y)
pixel_bottom = out.get_pixel(out.width-x-1, out.height - y - 1)
pixel_bottom.red = pixel.red
pixel_bottom.green = pixel.green
pixel_bottom.blue = pixel.blue
return out
def wave(filename, margin):
image = SimpleImage(filename)
#### Part a Create out ####
out = SimpleImage.blank(image.width + margin * 2, image.height * 2)
#### Part b Color in column ####
for y in range(image.height * 2):
for x in range(margin):
# right_col
pixel_r = out.get_pixel(margin + image.width + x, y)
pixel_r.green = 0
#### Part c Copy in reversed ###
for y in range(image.height): # loop over original
for x in range(image.width):
pixel = image.get_pixel(x, y)
pixel_out = out.get_pixel(margin + image.width - 1 - x, image.height + y)
pixel_out.red = pixel.red
pixel_out.green = pixel.green
pixel_out.blue = pixel.blue
return out
def do_image(filename, a, b):
image = SimpleImage(filename)
# a Create the out image
out = SimpleImage.blank(image.width, 2*image.height)
# b Color the yellow rectangle
for y in range(b):
for x in range(a):
pixel = out.get_pixel(x, y)
pixel.blue = 0
# c Copy the vertically flipped image
for y in range(image.height)
for x in range(image.width)
pixel = image.get_pixel(x, y)
pixel_out = out.get_pixel(x, b + image.height - 1 - y)
pixel_out.red = pixel.red
pixel_out.green = pixel.green
pixel_out.blue = pixel.blue
Functions
def digits_only(s):
result = ''
# Loop over all index numbers
for i in range(len(s)):
# Access each s[i]
if s[i].isdigit():
result += s[i]
return result
def lastly(s, n):
if len(s) == 0:
return s
# Start with s, loop to add on
result = s
for i in range(n):
# Add last char of s
result += s[len(s) - 1]
return result
def alpha2x(s):
result = '@'
for i in range(len(s)):
if s[i].isalpha():
result = result + s[i] + s[i]
result += '@'
return result
def alpha_start(s):
result = ''
for i in range(len(s)):
if s[i].isalpha():
result = result + '*' + s[i]
return result