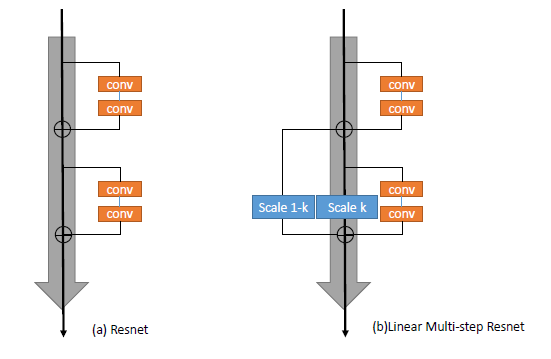
Continuous Depth Neural Network
Overview.To understand and improve the success of deep Residual Network, my research tends to limiting the depth of a Residual Network to infinity and comes out an ODE Model.
|
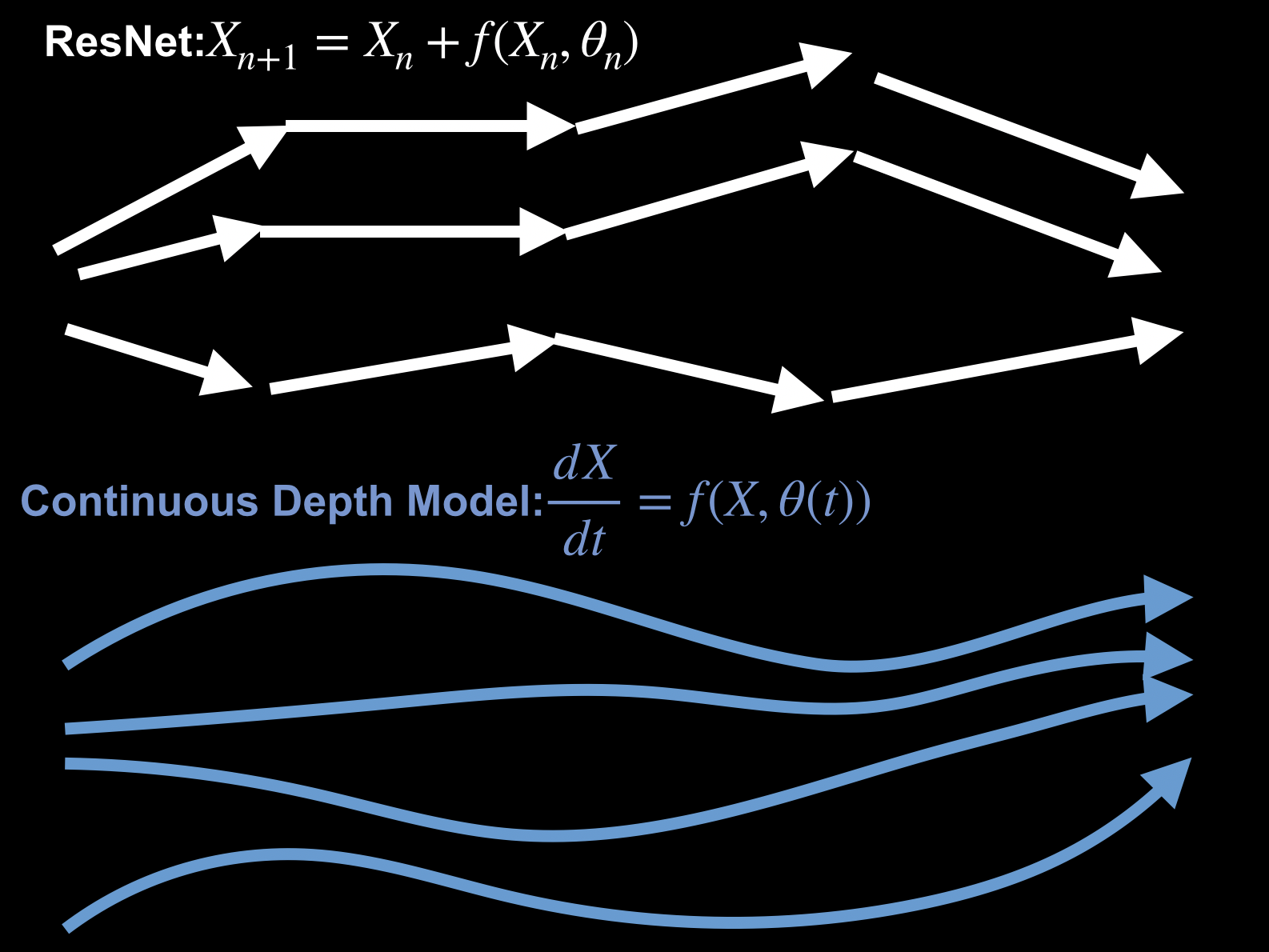 |
Optimization
How Continouos Depth Model Helps Understanding Optimization Of Deep Networks.
Using the ODE model can exploit the structure of Neural network while analysising the optimization. Based on Mean-field ResNet paper published at ICML2020 and YOPO paper published at NeurIPS2019.
Theory
|
We combined the ODE model and mean--field analysis of two-layer neural nets, we provide a convergence proof of training resnet beyond the lazy training regime. This is the first landscape result for deep neural networks in mean--field regime. Analysis of Wasserstein Gradient flow is still an open problem. |
||
Algorithm Design
|
ODE can help accelerate adversarial training!! Adversarial training doesn't need too many computational resources! We fully exploit structure of deep neural networks via recasting the adversarial training for neural networks as a differential game and propose a novel strategy to decouple the adversary update with the gradient back propagation. 4-5 times faster! |
||
Related Works
Here are the related papers by other groups.
- Li Q, Hao S. An optimal control approach to deep learning and applications to discrete-weight neural networks. ICML 2018.
- Liu G H, Chen T, Theodorou E A. Differential Dynamic Programming Neural Optimizer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.08809, 2020.
- Li X, Wong T K L, Chen R T Q, et al. Scalable Gradients for Stochastic Differential Equations. AISTATS 2020.
- Chen R T Q, Rubanova Y, Bettencourt J, et al. Neural ordinary differential equations Neurips2018.
- Chang B, Meng L, Haber E, et al. Multi-level residual networks from dynamical systems view. ICLR2018
- Günther S, Ruthotto L, Schroder J B, et al. Layer-parallel training of deep residual neural networks. SIMDOS 2020
Principled DL Model Desing
Our Finding:
1. Network Structure = Numerical Schemes
|
|
||||
2. Network should adapt to Task Physics
Using inverse problem as our application, to recover data from different level of degradation. We proposed appraoch solving the regularization path, which comes to a time-varing ODE whoese discretization should be a depth varying network.
Related papers:
- Chen Y, Yu W, Pock T. On learning optimized reaction diffusion processes for effective image restoration CVPR2015
- Wang X, Yu F, Dou Z Y, et al. Skipnet: Learning dynamic routing in convolutional networks. ECCV2018
- Chen X, Dai H, Li Y, et al. Learning to Stop While Learning to Predict. ICML2020
|
In this paper, we propose a new control framework called the moving endpoint control to restore images corrupted by different degradation levels in one model. The proposed control problem contains a restoration dynamics which is modeled by an RNN. The moving endpoint, which is essentially the terminal time of the associated dynamics, is determined by a policy network. Numerical experiments show that DURR can well generalize to images with higher degradation levels that are not included in the training stage. |
||
Related Works
Here are the related papers by other groups.
- Behrmann J, Grathwohl W, Chen R T Q, et al. Invertible residual networks ICML 2019.
-
- Zhang L, Wang L. Monge-ampere flow for generative modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.10188, 2018.
- Finlay C, Jacobsen J H, Nurbekyan L, et al. How to train your neural ode. ICML 2020.
- Tong A, Huang J, Wolf G, et al. TrajectoryNet: A Dynamic Optimal Transport Network for Modeling Cellular Dynamics. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.04461, 2020.
-
- Zhang J, Han B, Wynter L, et al. Towards robust resnet: A small step but a giant leap. IJCAI2019.
- Yang Z, Liu Y, Bao C, et al. Interpolation between Residual and Non-Residual Networks. ICML2020.
- Mingjie Li, Lingshen He, and Zhouchen Lin, Implicit Euler Skip Connections: Enhancing Adversarial Robustness via Numerical Stability, ICML 2020
-
- Chang B, Chen M, Haber E, et al. AntisymmetricRNN: A dynamical system view on recurrent neural networks. ICLR2019.
- Kag A, Zhang Z, Saligrama V. RNNs Incrementally Evolving on an Equilibrium Manifold: A Panacea for Vanishing and Exploding Gradients? ICLR2019.
- Chen Z, Zhang J, Arjovsky M, et al. Symplectic recurrent neural networks. ICLR2019.
-
- De Brouwer E, Simm J, Arany A, et al. GRU-ODE-Bayes: Continuous modeling of sporadically-observed time series Neurips2019
- Rubanova Y, Chen R T Q, Duvenaud D K. Latent ordinary differential equations for irregularly-sampled time series Neurips2019
- Cranmer M, Greydanus S, Hoyer S, et al. Lagrangian neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.04630, 2020.
Physics Applications
We made an initial attempt to learn evolution PDEs from data via Neural Networks.
Inspired by the latest development of neural network designs in deep learning, we propose a new feed-forward deep network, called PDE-Net, to fulfill two objectives at the same time: to accurately predict dynamics of complex systems and to uncover the underlying hidden PDE models. The basic idea of the proposed PDE-Net is to learn differential operators by learning convolution kernels (filters), and apply neural networks or other machine learning methods to approximate the unknown nonlinear responses.
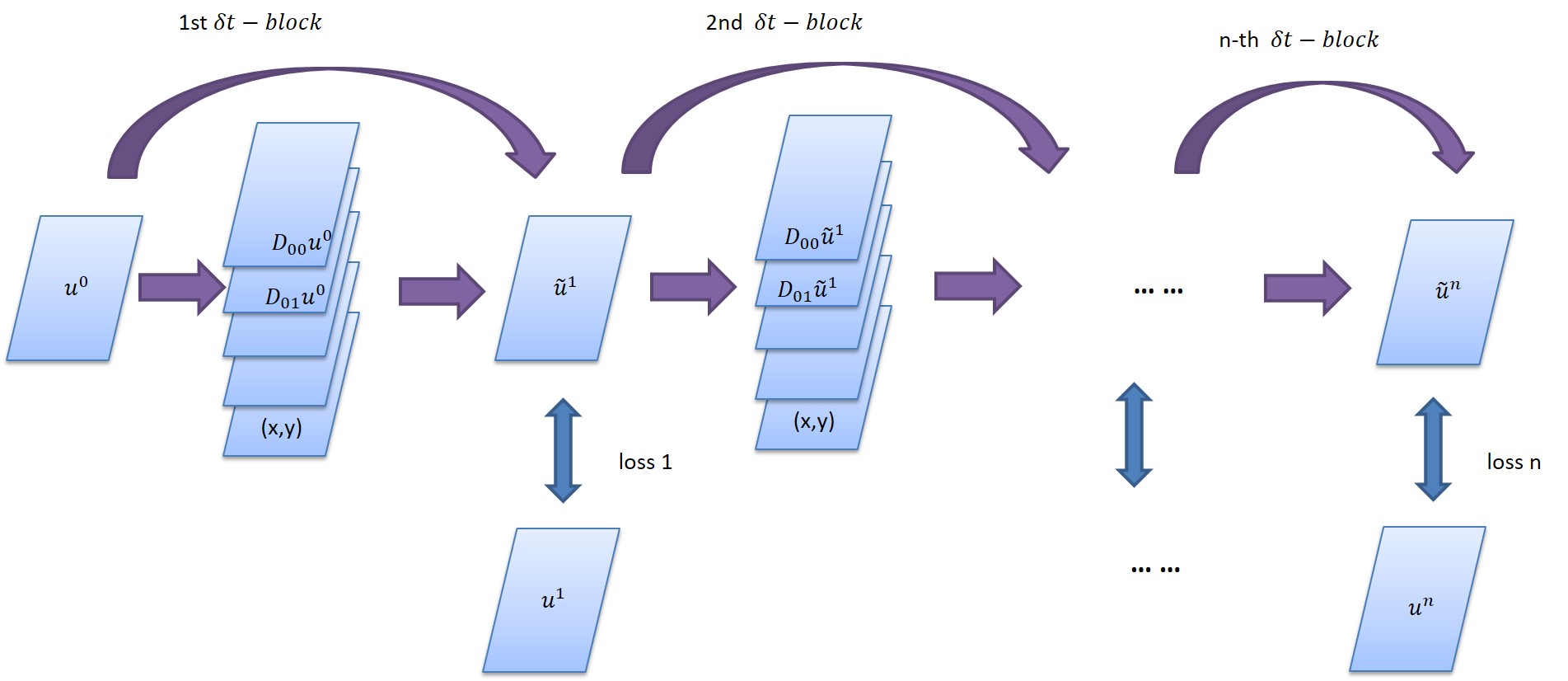
|
Zichao long*,
Yiping Lu*,
Xianzhong Ma*,
Bin Dong. "PDE-Net:Learning PDEs From Data",
Thirty-fifth International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2018(*equal contribution)
[ paper] [ arXiv] [ code] [ Supplementary Materials][ bibtex]
|

|
Zichao Long,
Yiping Lu,
Bin Dong. " PDE-Net 2.0: Learning PDEs from Data with A Numeric-Symbolic Hybrid Deep Network"
Journal of Computational Physics, 399, 108925, 2019.(arXiv preprint:1812.04426)
[ paper] [ arXiv] [code] [ slide] [ proceeding]
|
Related Works
- Raissi M, Karniadakis G E. Hidden physics models: Machine learning of nonlinear partial differential equations. Journal of Computational Physics, 2018, 357: 125-141.
- Brunton S L, Proctor J L, Kutz J N. Discovering governing equations from data by sparse identification of nonlinear dynamical systems. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences, 2016, 113(15): 3932-3937.
- Han J, Jentzen A, Weinan E. Solving high-dimensional partial differential equations using deep learning. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2018, 115(34): 8505-8510.
Contact Me
Stanford, CA, US
Phone: +86 18001847803
Email: yplu@stanford.edu
Let's get in touch. Send me a message: