[Menu] [Previous] [Next]
TUTORIAL: Clinical PET - Neurology
Use the "Menu" button to jump to the Let's Play PET Main Menu or click on the Next and Previous buttons to proceed sequentially through the topics and tutorials. Or, you can return to the Department of Molecular and Medical Pharmacology's Home Page.Contents:
Topics:
Neurological Trauma
Click on one or more of the images above to view full-size image(s).
PET has been used for many years to identify and study epileptogenic foci in human subjects. This FDG-PET scan comes from a young patient (15 months old) with severe, frequent epileptic seizures. One can see in these pre-operative images (obtained during an interictal period) that the cortex on one side of the brain is hypometabolic relative to the contralateral cortex.
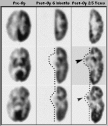
This series of scans was selected to illustrate the difference between acute and chronic trauma. Six months following hemidecortication, the brain-stem structures, although still present, have not recovered metabolically from the loss of their projections to and from the resected ipsilateral cerebral cortex. The images in the study on the left are in the superior view; those on the right are in the inferior view. The dotted border, derived from an MRI study, locates the anatomical edge of the brain tissue remaining post-operatively. Thus, in an acute injury, disconnection from the cerebrum causes the ipsilateral subcortical structures to be less metabolically active than normal.
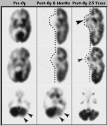
Thirty months following hemidecortication, the brain-stem structures have recovered metabolically from the loss of their projections to and from the removed ipsilateral cerebral cortex (arrows). This demonstrates the general principle that subcortical structures are metabolically preserved in chronic injury cases.
Credits
Material for this section was kindly provided by:Michael E. Phelps, Ph.D.
Dept. of Molecular and Medical Pharmacology
UCLA School of Medicine
Harry T. Chugani, M.D.
Pediatric PET Center
Children's Hospital
Wayne State University
[Menu] [Previous] [Next]